Full text: China's Green Development in the New Era(2)
时间:2024-02-22 17:36 来源:网络整理 作者:墨客科技 点击:次
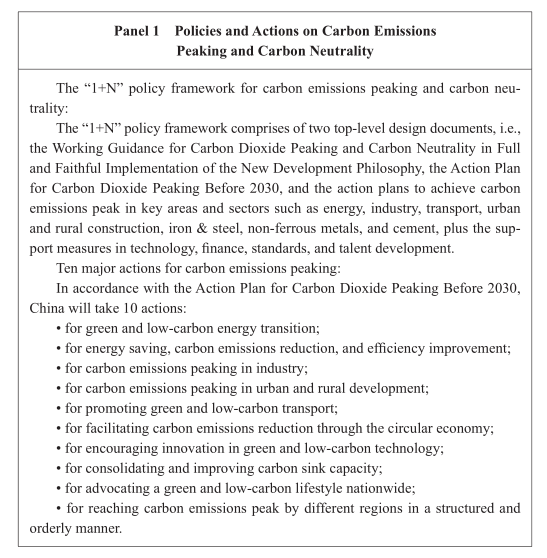
carbon emissions peak by 2030 and carbon neutrality by 2060. It will advance the green transition with these goals as the lead, play a more active part in bilateral and multilateral international cooperation on green development, promote a fair and equitable system of global environmental governance, and contribute its wisdom and strength to global sustainable development. II. A Basic Green Territorial Configuration Is in Place China is making efforts to optimize its governing system of territo- rial space. The country has strengthened the overall planning and coordi- nated management and control of territorial space for working and living and for the environment. It has intensified efforts to protect and restore ecosystems, effectively expanded the capacity of the eco-environment, and promoted the rapid accumulation of natural wealth and eco-environ- mental wealth, leading to historic, transformative, and comprehensive changes in eco-environmental protection and providing strong support for the sustainable and healthy development of the economy and society. 1. Optimizing the development and protection of territorial space A country’s territorial space is the carrier for green development. China has implemented a functional zoning strategy and established a unified territorial space planning system that is science-based, efficient and built upon clearly defined powers and responsibilities. Taking into consideration factors such as population distribution, regional economic structures, land use, and eco-environmental protection, it has planned for the development and protection of territorial space with a holistic ap- proach, so as to achieve higher-quality and more sustainable development of its territorial space. China has integrated different plans into a single master plan for ter- ritorial space development. It has integrated functional zoning, land use, urban and rural planning, and other spatial planning into a unified territo- rial space plan. A comprehensive system integrating planning approval, implementation supervision, regulations, policies and technical standards is taking shape. The role of territorial space planning has been strength- ened in guiding and constraining various specific plans. It has sped up the drafting of various plans for territorial space at all levels. As a result, an overall master plan will eventually be drawn up for the development and protection of territorial space. Concerted efforts have been made to optimize the use of territorial space. Based on the results of national land resource surveys, China has carried out an evaluation of the carrying capacity of resources and the environment, and suitability of land development. It has scientifically designated agricultural, ecological, urban and other functional zones, and improved the territorial space layout that consists of three major zones – main agricultural production zones, key ecosystem service zones and urbanized zones. To strengthen national and regional eco-environmental security, China has designated permanent basic cropland, drawn red lines for eco-environmental protection, delineated boundaries for urban devel- opment, and set protection lines for all types of sea areas, in a coordinated manner. It has established centralized control over the use of territorial space and ensured that these lines are not crossed. China has strengthened the management of key ecosystem service zones and endeavored to prevent and control eco-environmental risks. County- level administrative units that perform important ecological functions such as water conservation, soil and water conservation, inhibiting winds, fixing sand, and protecting biodiversity are designated as key ecosystem service zones, which should focus on protecting the environment and providing eco- environmental products and be restricted from large-scale industrialization and urbanization. As a result, China’s natural ecosystems are generally stable or improving, eco-environmental services have improved, and the supply of eco-environmental products has continued to increase. 2. Strengthening eco-environmental conservation and restoration Mountains, rivers, forests, farmland, lakes, grasslands and deserts are communities of life. China has stepped up systematic, comprehen- sive, and law-based environment governance, tackling problems at their sources. Prioritizing protection and focusing on natural restoration, it has vigorously pressed forward with the protection and restoration of ecosys- tems, so as to build a solid national eco-environmental security barrier and strengthen the foundations for the sustainable development of the Chinese nation. A new type of protected area (PA) system has been set up. PAs are major platforms for eco-environmental conservation. China is develop- ing a PA system with national parks as the mainstay, supported by nature reserves and supplemented by nature parks. It has created its first batch of five national parks – the Three-River-Source National Park, the Giant Panda National Park, the Northeast China Tiger and Leopard National Park, the Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park, and the Wuyishan National Park. It is making steady progress in building national parks in environmentally important regions. As of the end of 2021, nearly 10,000 PAs of various types and levels had been established, covering more than 17 percent of China’s land area, bringing under effective protection 90 percent of its natural terrestrial ecosystem types and 74 percent of key state-protected wildlife species. Setting up scientific eco-environmental conservation red lines (ECRLs). ECRLs are the lifeline of national eco-environmental security. China has brought functional areas of vital importance, exceedingly frag- ile areas, and areas of potentially vital eco-environmental value within the scope of the ECRL framework. More than 30 percent of China’s land area – including integrated and optimized PAs – is now under the protection of ECRLs. Through drawing ECRLs and drafting ecological protection and restoration plans, the country has consolidated an overall eco- environmental conservation configuration composed of Three Eco-zones and Four Shelterbelts – the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau Eco-zone, the Yellow River Eco-zone (including the Loess Plateau Ecological Barrier), the Yangtze River Eco-zone (including the Sichuan-Yunnan Ecological Barrier), and |