Full text: China's Green Development in the New Era(10)
时间:2024-02-22 17:36 来源:网络整理 作者:墨客科技 点击:次
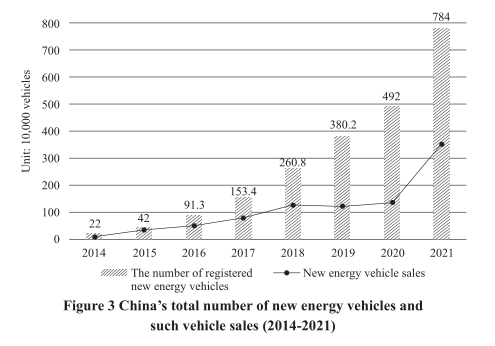
gas (LNG) powered boats and transformation of shore power facilities, and accelerated the transformation or elimination of obsolete vehicles and boats. Since 2012, more than 30 million yellow-label vehicles with high emissions have been eliminated, and 47,100 obsolete inland river boats have been re-engineered or mothballed. Upgrading transport infrastructure for green development. China has initiated a special program for the construction of green highways, and the recycling of waste road surface materials. By the end of 2021, more than 95 percent of the waste materials from expressways and 80 percent of the waste materials from national and provincial highways had been recycled. China has steadily improved afforestation along its roads. Green belts have been built along 570,000 kilometers of its trunk roads, about 200,000 kilometers more than in 2012. China has continued the electrifi- cation of its railways, with the proportion of electric railways increasing from 52.3 percent in 2012 to 73.3 percent in 2021. It has also built more green port and road transport support facilities. By the end of 2021, five types of shore power facilities had been built in 75 percent of the special- ized berths of major ports, and 13,374 charging piles had been built in ex- pressway service areas – the highest number in the world. 4. Promoting the economical and intensive use of resources As a country with a great demand for resources, China has acceler- ated the fundamental change in the way resources are utilized. To make a major contribution to the sustainable development of global resources and the environment, and to ensure a happy life for the people today as well as sufficient resources to meet the needs of future generations, China tries to obtain the maximum social and economic benefits at a minimum cost in resources and the environment. Improving the efficiency of energy use. China is exercising better control over the amount and intensity of energy consumption, particularly the consumption of fossil fuels. It has vigorously promoted technical, managerial, and structural energy conservation, to constantly improve the efficiency of energy use. It has initiated campaigns for all industrial enter- prises, especially the big consumers of energy, to save energy, reduce car- bon emissions, and improve the efficiency of energy use. The “forerunners” have been encouraged to play an exemplary role for other enterprises. China has organized the transformation of energy-intensive industries such as steel, power generation, and chemicals, to help them save energy and reduce carbon emissions. It has also strengthened the energy-saving management of key energy consumers, to enable large and medium-sized enterprises in key industries to reach advanced international levels in en- ergy efficiency. Since 2012, China’s average annual economic growth of 6.6 percent has been supported by an average annual growth of 3 percent in energy consumption, and the energy consumption per RMB10,000 of GDP in 2021 was 26.4 percent lower than in 2012. Improving the efficiency of water utilization. China has imposed in- creasingly rigid constraints on water use. Industrial and urban configura- tions are determined scientifically in accordance with water availability. China has launched nationwide water-saving campaigns to control the total amount and intensity of water consumption. It has upgraded water- saving technologies for industries with high water consumption, and pro- moted highly water-efficient irrigation for agriculture. It has advocated the building of water-saving cities, established a water efficiency labeling system, introduced certification standards for water conservation prod- ucts, and promoted the use of water-saving products and appliances. The comprehensive per capita water consumption in cities is falling steadily. China has also incorporated unconventional water sources, such as re- claimed water, desalinated seawater, collected rainwater, brackish water, and mine water, into the unified allocation of water resources, which has effectively eased the strain on demand in areas with a shortage of water. Water consumption per RMB10,000 of GDP in 2021 was 45 percent low- er than in 2012. Strengthening the economical and intensive use of land. China has improved the standards for urban and rural land use. The designation, standards and approval of land use for all kinds of construction projects are strictly controlled, and the economical and intensive use of land in the construction of transport, energy, and water infrastructure is encouraged. China has strengthened the management of rural land, and promoted the economical and intensive use of rural land for collective construction pro- jects. It has also established mechanisms for coordinating the use of exist- ing land resources and made the arrangements for additional resources, and for recovering idle land, in order to put all existing land resources to good use. From 2012 to 2021, the area of land designated for construction projects per unit of GDP decreased by 40.85 percent. Making scientific use of marine resources. China has strictly con- trolled land reclamation from the sea. It has prohibited all coastal recla- mation activities except those for major national projects, and dealt with problems left over from history in this regard with different approaches. It has established a control system to retain natural shorelines, and carried out classified protection and economical utilization of them. It has strictly protected uninhabited islands at sea and minimized their development and utilization. Ensuring the comprehensive use of resources. China has advocated the construction of green mines, promoted green exploration and exploi- tation, and worked to increase the recovery rate, processing recovery rate, and multipurpose utilization rate of major mineral resources. A total of 1,101 state-level green mines have been built. China has selected a total of 100 pilot projects and 100 backbone enterprises to promote the compre- hensive use of resources and started the construction of national demon- stration bases for recovering mineral resources from city waste. It has also updated the waste material collection network, coordinated the recycling of waste resources, and improved the processing and utilization of renew- able resources. In 2021, 385 million tonnes of nine renewable resources – waste iron and steel, copper, aluminum, lead, zinc, paper, plastic, rubber, and glass – were recycled for new purposes. V. Eco-Friendly Living Becomes the Prevailing Ethos Green development requires everyone’s efforts, and each of us can promote and practice green living. China actively promotes the values and ideas of eco-environmental conservation, raises public awareness to conserve resources and protect the eco-environment, and advocates the practice of a simpler, greener, and low-carbon lifestyle, creating a condu- cive social atmosphere for jointly promoting green development. 1. Continuing progress towards raising conservation awareness China places particular emphasis on cultivating its citizens’ conser- vation awareness. It organizes systematic publicity and other awareness- raising activities in this regard, and advocates a social environment and lifestyle of diligence and frugality. Publicity activities themed on National Energy-Saving Publicity Week, China’s Water Week, National Urban Water-Saving Week, National Low-Carbon Day, National Tree-Planting Day, World Environment Day, the International Day for Biological Di- versity, and Earth Day, are organized on a regular basis to encourage and persuade the whole of society to engage in green development activities. The idea of eco-friendly living has become widely accepted in families, communities, factories, and rural areas. Material on green development has been incorporated into China’s national education system through compiling textbooks on eco-environmental conservation and carrying out education in primary and secondary schools on the condition of national resources including forests, grasslands, rivers and lakes, land, water and grain. Respect for and love of nature have been advocated. Environmental Code of Conduct for Citizens (for Trial Implementation) was published to guide the public to follow a green lifestyle. As a result, a culture of eco- logical and environmental protection has joined the mainstream and been cherished by all. 2. Widespread initiatives to promote eco-friendly lifestyles China has launched initiatives to promote the building of resource- conserving Party and government offices, and develop eco-friendly families, schools, communities, transport services, shopping malls, and buildings, popularizing eco-friendly habits in all areas including cloth- ing, food, housing, transport, and tourism. To date, 70 percent of Party and government offices at and above county level are now committed to resource conservation, almost 100 colleges and universities have realized smart monitoring of water and electricity consumption, 109 cities have participated in green transport and commutes initiatives. Household waste sorting has been widely promoted in cities at or above prefecture level. Much progress is being made as residents gradually adopt the habit of sorting their waste. The Law of the People’s Republic of China on Food Waste has been enacted, and initiatives launched to promote food saving and curb food waste including a “clean plate” campaign on a large scale, which have yielded remarkable results as more people are saving food. 3. Growing market of green products China has actively promoted energy-saving and low-carbon products such as new-energy vehicles and energy-efficient household appliances. It has provided tax reductions or exemptions and government subsidies for new-energy vehicles and continued to improve charging infrastructure. As a result, the sales of new-energy vehicles have rapidly risen from 13,000 in 2012 to 3.52 million in 2021. For the seven years since 2015, China has ranked first in the world in the production and sales of new-energy ve- hicles. In addition, China has steadily improved the certification and pro- motion system for green products and the green government procurement system, implemented an energy efficiency and water efficiency labeling system to encourage the consumption of green products. It has promoted the construction of green infrastructure in the circulation sector such as green shopping malls, and supported new business models such as the sharing economy and second-hand transactions. There is a richer variety of green products and a growing number of people who spend on green products. VI. Improving the Institutions and Mechanisms for Green Development Sound institutions and mechanisms are essential to green develop- ment. With this understanding, China has stepped up efforts to create an eco-environmental conservation system based on clear orientation, sound decision-making, effective implementation, and strong incentives, and continued to improve government performance in promoting green devel- opment. This provides a solid guarantee for the realization of the coun- try’s green development goals. 1. Strengthening the rule of law China is committed to the rule of law in pursuing progress in eco- environmental conservation. It has written into its Constitution eco- environmental improvement and conservation, and promulgated and/or revised laws such as the Yangtze River Protection Law, the Yellow River Protection Law, the Land Administration Law, the Forest Law, the Grass- land Law, the Wetland Protection Law, the Environmental Protection Law, the Law on Environmental Protection Tax, the Law on the Prevention and Control of Atmospheric Pollution, the Law on the Prevention and Control of Water Pollution, the Law on the Prevention and Control of Soil Pollu- tion, and the Nuclear Safety Law. A legal system for eco-environmental conservation that covers all key areas, all types of resources, and all envi- ronmental factors has taken shape. China has also made consistent efforts to refine green development standards for key areas – more than 3,000 such standards have been formulated or amended. To better investigate and strictly punish violations of laws and regu- lations concerning natural resources and the eco-environment, China has reformed the system that places the monitoring, supervision, and law enforcement activities of environmental protection bodies below the pro- vincial level under the leadership of the same type of bodies at the imme- diate higher level. To strengthen coordination between the criminal justice system and law enforcement by government departments, China has es- tablished a system for procuratorates, courts, public security organs, and government departments responsible for coordinated law enforcement for environmental protection, enabling them to share relevant information, is- sue case briefings, and transfer cases among them. This has built a strong synergy for the investigation and punishment of environmental crimes, and provided powerful legal safeguards for green development. 2. Tightening supervision and management China has improved the performance evaluation system for green de- velopment, and taken strict measures to ensure that enterprises fulfill their principal responsibilities and that the government performs the duty of supervision in pursuing green development. GDP growth is no longer the sole criterion for the assessment of the development of regions or the per- formance of officials. Instead, binding targets concerning resources and the environment are set for economic and social development, and a more balanced assessment system for economic and social development is in progress – one that measures the use of resources, energy consumption, environmental damage, and the eco-environmental impact. This allows assessment to play its full guiding role in promoting green development. China has put in place an accountability system for leading officials, and formulated and/or revised a number of CPC regulations, including the Measures for Holding Leading Officials of the Party and the Government Accountable for Environmental Damage (for Trial Implementation), the Regulations on Central Environmental Inspections, and the Regulations on the Auditing of Natural Resource Assets for Leading Officials at the End of Their Tenures (for Trial Implementation). These are designed to ensure that Party committees and governments assume equal responsibili- ties for environmental protection, that leading officials perform their en- vironmental protection responsibilities with diligence, in addition to their other prescribed duties, and that they are held accountable when they fail to do so. China mandates end-of-tenure auditing of natural resource as- sets for leading officials, and imposes lifelong accountability for environ- mental damage. By implementing the central environmental inspection system, China has ensured that all parties concerned truly fulfill their re- sponsibilities for environmental protection, and has solved many environ- mental issues of pressing public concern. 3. Improving market-based mechanisms China is creating institutions and mechanisms for green development through which the government provides strong guidance, enterprises are fully engaged, and the market plays an effective role, thereby generating society-wide enthusiasm and participation. It has introduced new meas- ures to improve the pricing mechanisms in key areas such as water and energy saving, sewage and waste treatment, and air pollution control, adopted more than 50 preferential policies to cut taxes and fees, encour- aged better resource allocation, and supported conservation and efficient use of resources to advance green development. China has enforced a unified registration system for ownership of natural resources and an eco- environmental conservation compensation system that covers forests, grasslands, wetlands, deserts, water bodies and farmland. It is working on mechanisms for realizing the market value of ecosystem goods and services. China also encourages and supports private investment in envi- ronmental conservation and rehabilitation. On the base of a reasonable ceiling for total consumption, China has established initial allocation and trading systems for water, energy, pollution, and carbon permits. With the opening of the national carbon emissions trading market and trials in green electricity trading, progress is being made in allowing the market to play a fundamental role in the |